
第 1 页 / 共 21 页

第 2 页 / 共 21 页

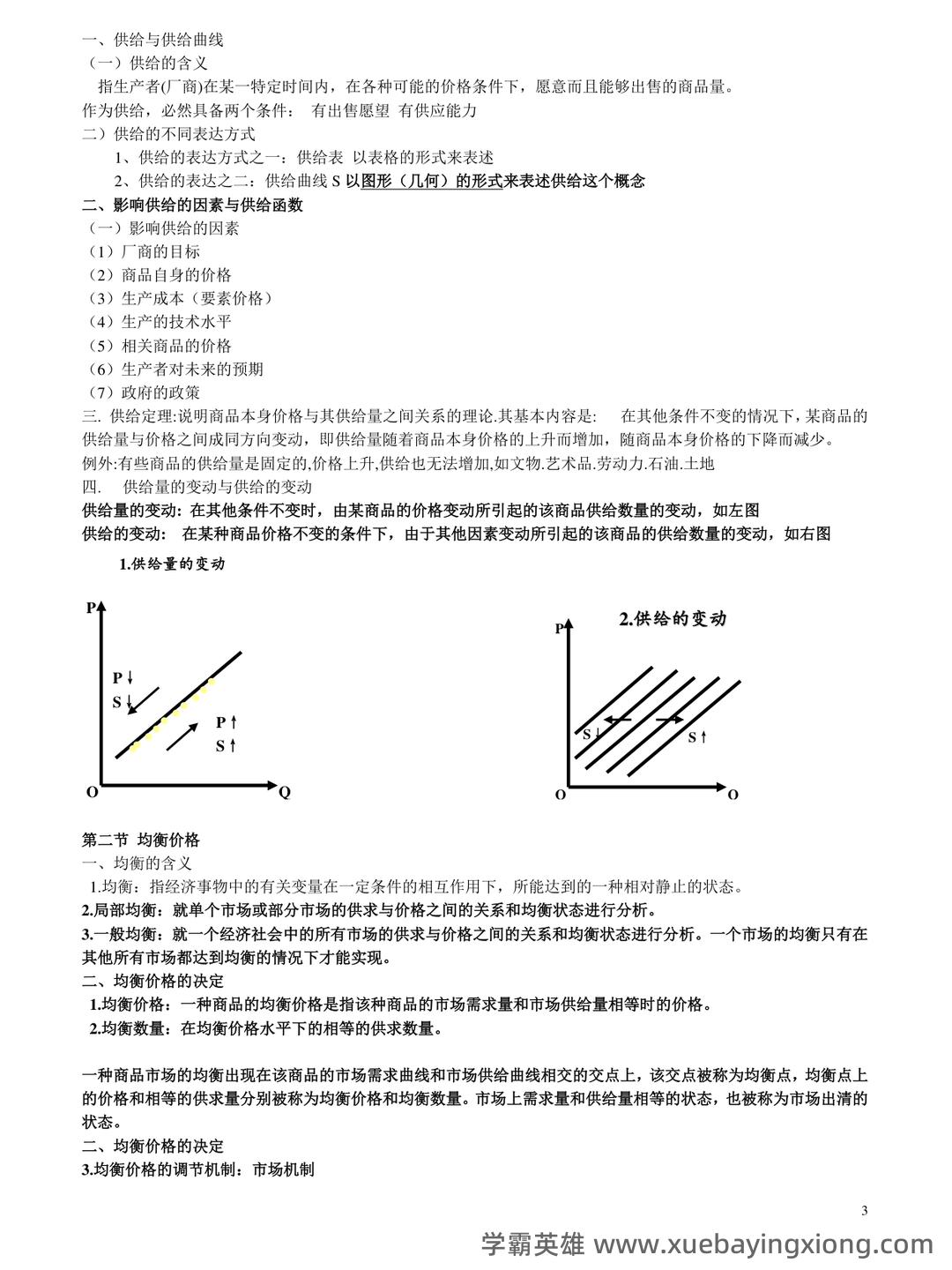
第 3 页 / 共 21 页

第 4 页 / 共 21 页

第 5 页 / 共 21 页
_第1页_学霸英雄_www.xuebayingxiong.com.png)
第 6 页 / 共 21 页
_第2页_学霸英雄_www.xuebayingxiong.com.png)
第 7 页 / 共 21 页

第 8 页 / 共 21 页

第 9 页 / 共 21 页
_第1页_学霸英雄_www.xuebayingxiong.com.png)
第 10 页 / 共 21 页
_第2页_学霸英雄_www.xuebayingxiong.com.png)
第 11 页 / 共 21 页
课后习题答案_第1页_学霸英雄_www.xuebayingxiong.com.png)
第 12 页 / 共 21 页
课后习题答案_第2页_学霸英雄_www.xuebayingxiong.com.png)
第 13 页 / 共 21 页

第 14 页 / 共 21 页

第 15 页 / 共 21 页

第 16 页 / 共 21 页
第 17 页 / 共 21 页

第 18 页 / 共 21 页

第 19 页 / 共 21 页
第6版课后习题答案详解_第1页_学霸英雄_www.xuebayingxiong.com.png)
第 20 页 / 共 21 页
第6版课后习题答案详解_第2页_学霸英雄_www.xuebayingxiong.com.png)
第 21 页 / 共 21 页
西方经济学名词解释_英文版
Western Economics Terminology Explained The field of Western economics is a vast landscape of concepts, often intimidating for newcomers. But at its core, it’s built upon a set of fundamental terms – terms that shape how we understand markets, resources, and ultimately, how societies function. Let’s unpack some of the key jargon, moving beyond the textbook definitions. First, you’ll encounter “Opportunity Cost.” This isn’t just about the price tag; it’s the value of the next best alternative you forgo when making a decision. Think about choosing to spend an hour studying – the opportunity cost might be the enjoyment you could have had playing a game. It’s a crucial element in rational economic decision-making. Then there's “Scarcity,” a bedrock principle. Western economics fundamentally rests on the idea that resources – land, labor, capital – are finite. This scarcity drives competition and shapes our choices. It’s not a shortage of everything, but rather a lack of something relative to our desires. Next, consider “Supply and Demand.” This model is arguably the most important in understanding market dynamics. It postulates that prices are determined by the interaction of what consumers want (demand) and what producers are willing to offer (supply). Shifts in either factor dramatically impact prices. Finally, “Elasticity” is a vital concept, particularly when discussing the responsiveness of supply and demand. It measures how much the quantity demanded or supplied changes in response to a change in price. High elasticity means a big reaction; low elasticity means a muted one. Understanding these terms – and the underlying assumptions – is the first step toward navigating the complexities of Western economics. It’s about recognizing that decisions, both individual and societal, are always made within the context of scarcity and shaped by our perceptions and values.
展开
西方经济学
2025-08-01
36次阅读